Technology Innovation to Accelerate Growth was the theme of a recent innovation workshop and tour of MIT’s Innovation Headquarters (iHQ) in Cambridge Massachusetts, in the heart of Kendall Square. The locale, known as “the most innovative square mile on the planet,” is home to MIT’s thriving community of innovators and entrepreneurs. The full-day event was sponsored by Frost & Sullivan’s Growth Innovation Leadership Council, which aims to achieve transformational growth for members and their companies through enlightened leadership. Thought leaders from Intel, GE Digital, Dell Technologies, True Car, Inc. and other companies shared current innovation insights and strategies – with a focus on those that intersect with technology – and collaborated with peers.
The agenda included sessions on technology and growth; AI and automation; fostering growth through sustainability; and breaking through the labor crisis; among other timely topics.
Here are just some of the highlights and ideas shared:
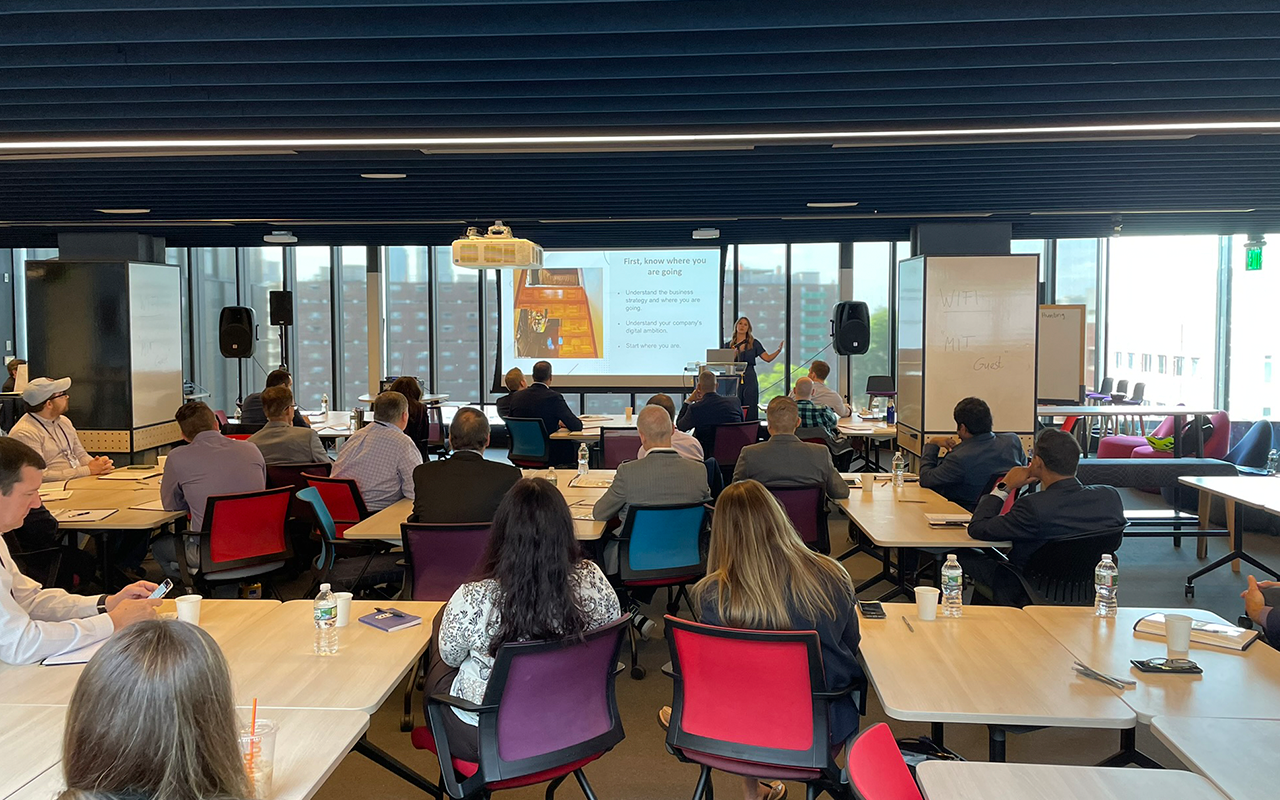
Technology Strategy to Create Customer Value and Drive Growth
Katie Webb, Director, U.S. Innovation, Aflac, opened the workshop by advising participants to know their company and its strengths and to view strategy as a three-legged stool. As she stated, “It’s not just about the technology, the business, or the customer – you need all three for a sturdy stool or strategy.”
Participants were encouraged to re-imagine the role of technology in their own organizations and leverage it as a business driver. Push technologies, which are implemented when information is transferred from a server without a request from the client, were distinguished from pull technologies, where a client or user requests data from a server. Both have useful strategic and tactical applications.
As noted, some of the strategies that helped Aflac transform itself into a digital organization included the critical first step of building trust among team members, determining how to optimize processes, and most importantly, making it easier for customers to buy products, distribution teams to sell products, and employees to be productive. The company transformation included re-creating what products looked like using digital technologies, and resulted in new ways of working, selling and serving customers. Best practices shared included identifying, prioritizing and validating strategies and themes, then building appropriate teams and embedding the strategy and roadmap – and most critically, doing this continuously.
Executive Insight – Fostering Growth Through Sustainable Innovation
Julie Newman, Ph.D., Director of Sustainability, at the MIT Office of Sustainability, discussed how her team leverages the campus as a test bed to design, test, scale and accelerate climate and sustainability solutions. As she noted, these solutions range from technical to social, and span the individual, the campus, the city, the state, the nation, and the globe. As stated, “Institutions of higher education committed to sustainability must be willing to act as test beds and models in the process.” Demonstrating this, the MIT Office of Sustainability seeks sustainable solutions by combining research and course engagement and using the campus as a test bed. One key Office of Sustainability resource is the Sustainability Data Pool, an open platform that allows their 24,000+ community access to the same data on energy, waste, and water and allows users to track it over time. The end goal: generating game-changing solutions to global challenges.
Setting an example, the building in which the Innovation Headquarters (iHQ) the Office of Sustainability, and other MIT departments are located, is one of the most energy efficient buildings on campus and was built to a LEED Gold V4 standard. Every material in the building was selected from a sustainability-focused source. A major initiative is reducing carbon emissions. Another example of sustainable innovation can be found in The Hive, MIT’s sustainability garden. It is a collaborative project between the Office of Sustainability, the Undergraduate Association Committee on Sustainability (UA Sustain), and MIT Grounds Services. The Hive aims to bring the community together for sustainability education, collaborative thinking, and mindfulness.
Newman recommended that leaders exchange sustainability ideas and strategies with other organizations to help reinforce and grow toolkits and optimize efforts. Sharing ideas and collaborating often helps sustainability goals be realized more quickly. Another key initiative on MIT’s horizon is power grid modernization. To bring this project and others like it to fruition faster, leaders are advised to continuously ask questions such as:
- How do we prepare and contribute to a new energy future?
- What can we adapt, and when?
- What is the role of AI in helping to reduce energy consumption?
- What are the opportunities for interventions?

Executive Insight – Harnessing the Real Potential of AI and Automation
Sabyasachi Roy, Ph.D., Head of Innovation & Strategy and Software Systems Design, Regulatory Affairs at Philips, discussed AI and its promise to fundamentally transform healthcare delivery, particularly in the area of medical devices. Sabyasachi stated, “Global healthcare systems are facing severe challenges including chronic disease burden, deficit of skilled healthcare professionals, increasing costs, increasing waste and increased demand for value-based care. AI will hopefully be part of the solution, but it’s not the silver bullet.”
Some of the ways AI can help include earlier disease detection, more accurate diagnoses, new insights into human physiology, personalized diagnostics and therapeutics and a reduced burden on healthcare providers. Some of the challenges include the fact that AI is often seen as a black box whose operations aren’t fully visible to users, resulting in reduced trust and slow adoption. Sabyasachi outlined the typical process flow of AI in medicine, which includes input – text data, image/video data, biometric data; analysis – rule based, deep learning; and output – classification and diagnosis.
Speaking about AI and medical devices, he shared these implementation guidelines:
- Engage with the regulator(s) early. Know your data and algorithm, and be concise about describing the functionality you’re trying to market and how you’ll ensure robustness
- Clearly define functionality of AI and segregate it from non-regulated software
- Implement good machine learning practices in your development process
- Gauge the level of validation required to establish safety and effectiveness
- Pay attention to your validation plan and monitor performance once the device is released
- Implement change control process suitable for AI and align with regulator(s) on when a device requires re-authorization
Medical and Healthcare is one of the largest focus areas receiving private investment in AI today. As widely referenced, a robust regulatory framework for AI is needed, now more than ever. Currently, there isn’t a globally harmonized regulatory approach for AI/ML device software. However, regulators including the US Food and Drug Administration, European Commission, and China’s National Medical Products Association (NMPA) are in the process of implementing their specific regulatory framework.
Capstone – The Labor Crisis: Breaking Through Significant Barriers to Innovation and Growth
Michelle Garcia Dorminey, Former Vice President, Innovation, TrueCar, Inc., addressed the fact that the current labor crisis poses a significant challenge for companies pursuing innovation and growth. Dorminey offered tools and insights to help flip the narrative from “We need to solve the labor crisis in order to innovate” to “We need to be innovative in order to solve our labor crisis.” Key insights included:
- Start looking at different roles and take advantage of opportunities to hire people who can bring new ideas to the table
- Look to establish collaboration across all departments, instead of focusing on vertical goals
- We know that collaboration = innovation, so put new and necessary systems in place to enable that
- Identify and nurture employee talent and strengths, including:
- All-stars (innovators)
- Rock-stars (producers)
- Provide upskilling opportunities for employees that will help them embrace an innovation mindset
- Leverage the fact that different perspectives can solve problems more quickly – reframe the situation
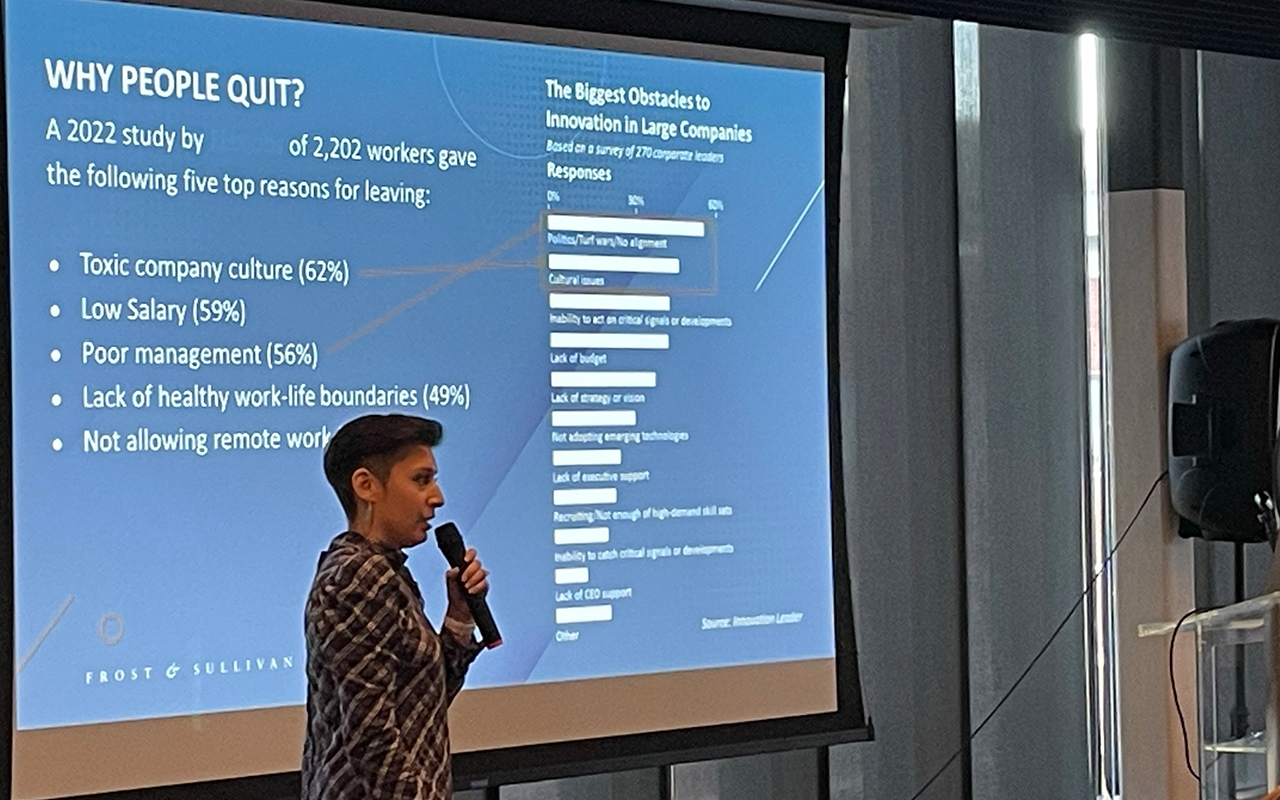
Dorminey also discussed leadership’s role in fostering innovation. She advocated for a flat organizational structure buoyed by a strong leadership team and a culture that is comfortable with failure. Inspiring play and personal accountability were also viewed as foundational to an innovative and healthy workplace and to attracting and keeping talent in today’s labor crisis.
These are just some of the insights and implementable ideas shared at MIT InnovationHQ. Look for an e-Magazine that will offer a deeper dive and key takeaways from the entire event, including the tour, in the coming weeks.
The Growth Innovation Leadership Council will be hosting their next Innovation Workshop and Tour: A Quarterly Series, at NASA Space Center in Houston, Texas on September 13th. The event will feature a guided tour of the NASA Johnson Space Center and an agenda focused on New Product Innovation and Development to Accelerate Growth. Click here to learn more or register today!



Recent Comments