This blog is based on Frost & Sullivan’s analysis Enhancing Grid Resilience: Emerging Technologies for Modern and Reliable Power Systems by Frost & Sullivan’s growth experts Heena Juneja and Monica Chabbra, from the TechVision Information & Communication Technologies team.
The power grid is the backbone of modern economies, enabling electricity transmission from generation facilities to consumers across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Yet today’s grids are under pressure from rising energy demand, aging infrastructure, extreme weather events, and cyber threats. Resilient grids, equipped with redundancy and advanced digital technologies, are essential for ensuring public safety, enabling renewable energy integration, and reducing costly downtime. By 2032, the global smart grid market is forecast to reach $216.40 billion, with grid resilience technologies alone expanding to $79.68 billion.
How is your organization ensuring that grid transformation strategies are aligned with future resilience and renewable integration goals?
| Grid Infrastructure Investments: Global Outlook |
Is your organization prepared to capture growth opportunities in grid modernization across advanced and emerging markets? |
| Download Frost & Sullivan’s Sample or connect with our experts at [email protected] to explore regional strategies for resilient grid investments. |
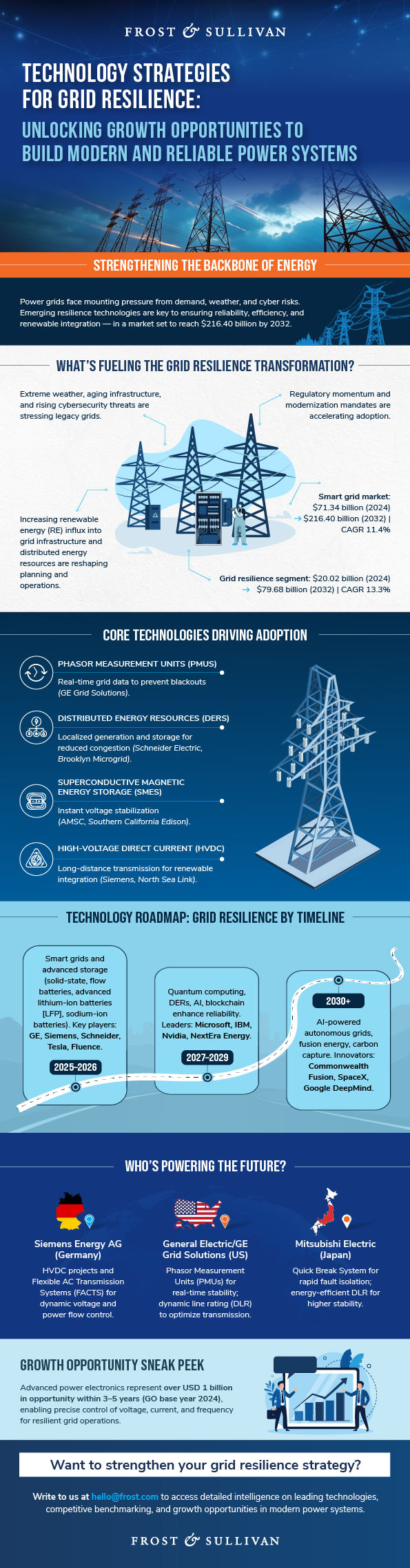
Emerging Technologies Shaping Grid Resilience
- Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs): Delivers real-time electrical wave data to prevent blackouts. GE Grid Solutions has equipped National Grid with PMUs to improve system reliability.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): Small-scale systems such as solar panels and microgrids decentralize generation. Schneider Electric’s Brooklyn Microgrid project demonstrates DERs’ role in reducing congestion.
- Superconductive Magnetic Energy Storage (SMES): SMES stabilizes voltage by discharging energy instantly. American Superconductor (AMSC) deployed SMES at Southern California Edison to prevent short-term fluctuations.
- High-voltage Direct Current (HVDC): Efficiently transmits power across long distances. Siemens implemented HVDC in the North Sea Link, integrating renewable power between the UK and Norway.
Which emerging technologies will shape your roadmap for delivering resilient, future-ready power systems?
| To know more about other emerging technologies like microgrids, energy storage, and demand response management systems (DRMS), download the full study or write to [email protected] |
Strategic Imperatives Reshaping Grid Resilience
- Innovative Business Models: Utilities are monetizing resilience through demand response programs, dynamic pricing, and energy-as-a-service models that optimize operations and create new revenue streams.
- Competitive Intensity: Artificial intelligence (AI), advanced sensors, and distributed networks are intensifying competition. Utilities must innovate quickly to integrate renewables and maintain reliability.
- Disruptive Technologies: HVDC, advanced automation, and energy storage systems are redefining how grids withstand modern challenges and adapt to future demands.
What best practices is your organization adopting to align innovation, investment, and operational strategies with grid resilience imperatives?
| Future of Power Grid Resilience: Short-, Mid-, and Long-term Outlook |
Is your organization prepared to align its short-, mid-, and long-term strategies with the future direction of grid resilience technologies? |
| Download Frost & Sullivan’s study Enhancing Grid Resilience: Emerging Technologies for Modern and Reliable Power Systems, or connect with our experts at [email protected] to plan your roadmap today. |
Companies to Action
- Siemens Energy AG (Germany): Focuses on grid automation, smart grids, energy storage, and microgrids. Uses flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS) for dynamic control of voltage and power flow.
- General Electric (GE, US): Provides grid management, HVDC, and renewable integration solutions. GE’s dynamic line rating (DLR) technology adjusts line capacity based on real-time weather conditions.
- Mitsubishi Electric (Japan): Quick Break System enables rapid isolation of faulty grid segments to prevent cascading failures. Its DLR solutions enhance grid efficiency and stability in variable load conditions.
How confident are you that your organization is partnering with the right innovators to strengthen its competitive edge in grid resilience?
Why This Matters Now
Grid resilience is no longer optional. It is a cornerstone of safe, reliable, and sustainable power systems. From PMUs to HVDC projects, emerging technologies are redefining how utilities address growing energy demand, integrate renewables, and mitigate risks. Organizations are embracing innovative business models, invest in disruptive technologies, and partner with global leaders will not only enhance resilience but also capture significant long-term growth in a market set to exceed $79.68 billion by 2032.
Want to dive deeper?
Connect with us to explore how these insights can help strengthen your organization’s power grid resilience strategy. Schedule a complimentary Growth Pipeline Dialog™ with our experts to uncover tailored opportunities for modernization and reliability.



